Polluted aquifer inverse problem solution using artificial neural networks
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
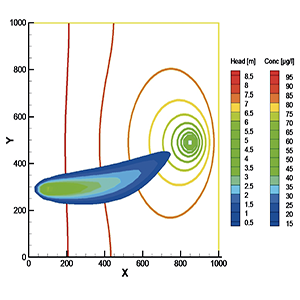
The problem of identifying an unknown pollution source in polluted aquifers, based on known contaminant concentrations measurement in the studied areas, is part of the broader group of issues, called inverse problems. This paper investigates the feasibility of using Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) for solving the inverse problem of locating in time and space the source of a contamination event in a homogeneous and isotropic two dimensional domain. ANNs are trained in order to implement an input-output relationship which associates the position. Once the output of the system is known, the input is reconstructed by inverting the trained ANNs. The approach is applied for studying a theoretical test case where the inverse problem is solved on the basis of measurements of contaminant concentrations in monitoring wells located in the studied area. Groundwater pollution sources are characterized by varying spatial location and duration of activity. To identify these unknown pollution sources, concentration measurements data of monitoring wells are used. If concentration observations are missing over a length of time after an unknown source has become active, it is more difficult to correctly identify the unknown pollution source. In this work, a missing data scenario has been taken into consideration. In particular, a case where only one measurement has been made after the pollutant source interrupted its activity has been considered.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.














