Modeling groundwater/surface-water interactions and their effects on hydraulic barriers, the case of the industrial area of Mantua (Italy)
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
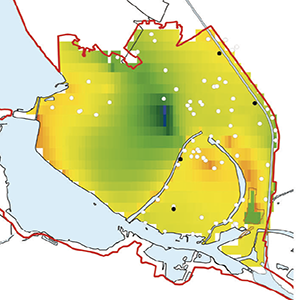
The town of Mantua is a good example of an urban area with an intricate surface water system leading to complex groundwater/surface-water interactions. In this context, the Site of National Interest (SIN) “Laghi di Mantova e Polo Chimico”, is characterized by intense pumping activity by means of industrial wells and hydraulic barriers. In order to establish the interactions between groundwater and the surface water system, evaluating their relation with the pumping activities, a transient groundwater numerical model was developed (January 2016 - December 2018) using MODFLOW-2005 and the Streamflow-Routing (SFR2) package, following a participatory approach. Results show how, depending on the minimum/ maximum groundwater conditions and the discharge values of the surface channels, the relation between groundwater/surface-waters can vary during the year, also affecting the operation of the hydraulic barriers. The stakeholders could use the calibrated model in the future to ensure optimal management of the pumping activities within the SIN.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.














